Bitcoin
Inside the ‘Nightmare’ Health Crisis of a Texas Bitcoin Town

On an evening in December 2023, 43-year-old small business owner Sarah Rosenkranz collapsed in her home in Granbury, Texas and was rushed to the emergency room. Her heart pounded 200 beats per minute; her blood pressure spiked into hypertensive crisis; her skull throbbed. “It felt like my head was in a pressure vise being crushed,” she says. “That pain was worse than childbirth.”
Rosenkranz’s migraine lasted for five days. Doctors gave her several rounds of IV medication and painkiller shots, but nothing seemed to knock down the pain, she says. This was odd, especially because local doctors were similarly vexed when Indigo, Rosenkranz’s 5-year-old daughter, was taken to urgent care earlier that year, screaming that she felt a “red beam behind her eardrums.”
It didn’t occur to Sarah that these symptoms could be linked. But in January 2024, she walked into a town hall in Granbury and found a room full of people worn thin from strange, debilitating illnesses. A mother said her 8-year-old daughter was losing her hearing and fluids were leaking from her ears. Several women said they experienced fainting spells, including while driving on the highway. Others said they were wracked by debilitating vertigo and nausea, waking up in the middle of the night mid-vomit.
None of them knew what, exactly, was causing these symptoms. But they all shared a singular grievance: a dull aural hum had crept into their lives, which growled or roared depending on the time of day, rattling their windows and rendering them unable to sleep. The hum, local law enforcement had learned, was emanating from a Bitcoin mining facility that had recently moved into the area—and was exceeding legal noise ordinances on a daily basis.
Over the course of several months in 2024, TIME spoke to more than 40 people in the Granbury area who reported a medical ailment that they believe is connected to the arrival of the Bitcoin mine: hypertension, heart palpitations, chest pain, vertigo, tinnitus, migraines, panic attacks. At least 10 people went to urgent care or the emergency room with these symptoms. The development of large-scale Bitcoin mines and data centers is quite new, and most of them are housed in extremely remote places. There have been no major medical studies on the impacts of living near one. But there is an increasing body of scientific studies linking prolonged exposure to noise pollution with cardiovascular damage. And one local doctor—ears, nose, and throat specialist Salim Bhaloo—says he sees patients with symptoms potentially stemming from the Bitcoin mine’s noise on an almost weekly basis.
Cheryl Shadden’s homemade signs on her property across the street from the mine.
“I’m sure it increases their cortisol and sugar levels, so you’re getting headaches, vertigo, and it snowballs from there,” Bhaloo says. “This thing is definitely causing a tremendous amount of stress. Everyone is just miserable about it.”
Not all data centers make noise. And industry insiders say they have a technical fix for the ones that do, which involves replacing their facilities’ loud air fans with much quieter liquid-based cooling solutions. But some of their touted methods, including “immersion cooling” in oil, are expensive and untested on a large scale.
A representative for Marathon Digital Holdings, the company that owns the mine, did not answer questions about health impacts, but told TIME that it is working to remove the noisy fans from the site. “By the end of 2024, we intend to have replaced the majority of air-cooled containers with immersion cooling, with no expansion required. Initial sound readings on immersion containers indicate favorable results in sound reduction and compliance with all relevant state noise ordinances,” they wrote in an email.
The number of commercial-scale Bitcoin mining operations in the U.S. has increased sharply over the last few years; there are now at least 137. Similar medical complaints have been registered near facilities in Arkansas and North Dakota. And the Bitcoin mining industry is urgently trying to push bills through state legislatures, including in Indiana and Missouri, which would exempt Bitcoin mines from local zoning or noise ordinances. In May, Oklahoma governor Kevin Stitt signed a “Bitcoin Rights” bill to protect miners and prevent any future attempts to ban the industry.
While some Granbury residents are fiercely protesting the mine, many others feel powerless to alter the will of a company with legal, political, and financial might. And the data center industry at large is only growing more dominant, thanks to the twin forces of Bitcoin mining and AI, the latter which spends a vast amount of energy training generative models to find patterns in data sets. According to a recent report, data centers will use 8% of total U.S. power by 2030, up from 3% in 2022. And if operators continue to locate the centers near existing communities and prioritize profits above all else, then the story of Granbury could become the story of countless small towns across America.
Granbury sits about an hour southwest of Fort Worth in Hood County, which houses a mostly rural and Republican population of about 65,000 people. About a 15-minute drive south of Granbury’s charming historic town center—which includes a 19th-century opera house—lies a gas plant called Wolf Hollow II. Driving toward the plant on a windy, predawn morning in May, it rises out of the sky like an oil rig in a pitch-black ocean, lights ablaze.
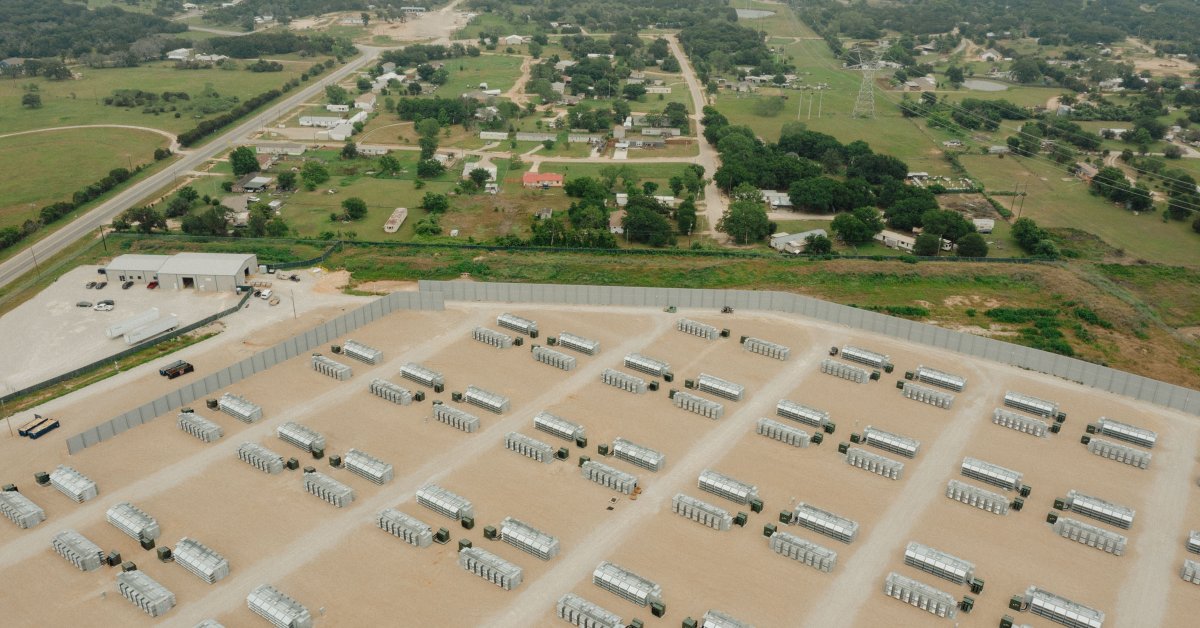
But the glowing gas plant never caused substantial issues for the local residents. Rather, the problems started when Constellation Energy, which operated the plant, signed a deal in 2021 to power a new Bitcoin mining facility that would sit directly on its lot. The new facility consisted of 163 squat metal boxes resembling shipping containers, which housed a total of over 30,000 computers. These computers started running in the summer of 2022, and seemed to be switched on all day and night. As of December 2023, the Granbury mine is owned and operated by Marathon, one of the largest Bitcoin holders in the world.
 Constable John Shirley, a former Oath Keeper, has been focused on keeping the mine accountable.
Constable John Shirley, a former Oath Keeper, has been focused on keeping the mine accountable. Shirley takes sound readings near the Wolf Hollow data site on May 20, 2024.
Shirley takes sound readings near the Wolf Hollow data site on May 20, 2024.
The computers power a process called proof-of-work mining. Rather than relying on a central bank or governmental agency, Bitcoin is created, maintained, and guarded by watchdogs around the world known as miners, who prevent tampering through a complex cryptographic process and are rewarded with bitcoin for doing so. Bitcoin’s first supporters hoped that this new system would support a global digital currency that would bring freedom, financial fairness, and wealth to its adopters.
But the system also requires an immense and ever-increasing amount of electricity. While Bitcoin’s first miners were solo operators often working out of their bedrooms, the industry is now dominated by a handful of billion-dollar corporations who operate industrial-size server farms across the globe. In the month of March 2024 alone, the Bitcoin mining industry generated a record $2 billion in revenue.
Much of the American Bitcoin mining industry can now be found in Texas, home to giant power plants, lax regulation, and crypto-friendly politicians. In October 2021, Governor Greg Abbott hosted the lobbying group Texas Blockchain Council at the governor’s mansion. The group insisted that their industry would help the state’s overtaxed energy grid; that during energy crises, miners would be one of the few energy customers able to shut off upon request, provided that they were paid in exchange. After meeting with the lobbyists, Abbott tweeted that Texas would soon be the “#1 [state] for blockchain & cryptocurrency.” The following month, the Commissioners Court of Hood County approved the development of a cryptocurrency operation at Wolf Hollow. The owners promised local jobs and said that they would mostly use “stranded energy” that would otherwise go unused.
For months during 2022, Granbury residents Nick and Virginia Browning sat in their front yard watching the new metal boxes of the massive facility be installed in the dirt across the road. “It layered our houses with dust. We haven’t gotten it all out yet,” Nick Browning, 82, says.
The dust, it turns out, was just a prelude to the noise. In order to cool the machines, the site’s operators attached thousands of fans to the containers, which churned constantly, emitting a vicious buzz. As more machines were switched on, the noise sounded like a ceiling fan, then a leaf blower, then a jet engine. It consumed afternoon dog walks and revved through cloudless nights, vibrating the trailer homes of many of the low-income residents who live blocks from the facility. The noise floated miles down the winding Brazos river, through the lush golf courses in the gated community Pecan Plantation and past county lines.
At first, residents responded to the intrusion by vacating their porches, retreating inside, and turning up their fans and air conditioners to the max. But many still felt tremors in their beds—including Larry Potts, a 77-year-old retired pastor who lives up the road from the plant. Potts says he stopped sleeping and started losing hearing in both ears. In February, his heart gave out after another sleepless night; he was rushed to the hospital and kept alive by an external pacemaker. There, he was diagnosed with third degree atrioventricular block, hypertension, and depression.
 Larry Potts at his home in Granbury, Texas. He suffered from heart failure in February.
Larry Potts at his home in Granbury, Texas. He suffered from heart failure in February.
“I’m sick of this world and all this mess around here,” he says he told his wife that day, referring to the Bitcoin mine’s noise. “We moved out here for the peace and quiet. But this has made me want to go.”
Some nearby residents say they haven’t been affected. But the number of strange medical emergencies in the area have piled up. In addition to Potts’ discharge papers, TIME reviewed medical records provided by several Granbury residents. Hospital notes from 72-year-old Geraldine Lathers’ three-day stay document new prescriptions for high blood pressure and vertigo. Jenna Hornbuckle, 38, lost hearing in her right ear and was diagnosed with heart failure; ear exams document her hearing loss along with that of her 8-year-old daughter Victoria, who contracted ear infections that forced doctors to place a tube in her ear. And Avari Burns, a 19-year-old cancer patient, says she suffered from crippling migraines at home—but whenever she went to a Fort Worth hospital for chemotherapy, the migraines subsided.
Virginia Browning, 81, who can see the Bitcoin mine from her front yard, says she was taken to urgent care with violent vertigo after waking up one night mid-vomit. Browning says she gets so dizzy she can barely walk in a straight line, and that she rarely sleeps through the night. “When they crank this thing,” she says shakily, “I’m wide awake.”
“We’re living in a nightmare,” Sarah Rosenkranz says, sitting at a barbecue restaurant in downtown Granbury on an evening in May. As rock music blares from the speakers and other patrons chatter away, Rosenkranz pulls out her phone and clocks 72 decibels on a sound meter app—the same level that she records in Indigo’s bedroom in the dead of night. In early 2023, her daughter began waking up, yelling and holding her ears. Indigo’s room directly faces the mine, which sits about a mile and a half away. She soon refused to sleep in her own room. She then developed so many ear infections that Rosenkranz pulled her from school in March and learned how to homeschool her for the rest of the semester.
Over grilled salmon and hush puppies, Rosenkranz shares that her family has been sleeping peacefully at an inn downtown for the last three days in order to get away from the noise. But the next morning, after returning home, she contracts yet another migraine that lands her in urgent care.
Dr. Bhaloo, the ENT doctor in Granbury, says he’s seen an uptick since the new year in patients whose ailments—including ringing in their ears, vertigo, and headaches—could be related to the mine. “These people here, they’re good country folks, and Bitcoin, to them, is almost a foreign alien thing,” he says. “They don’t understand it. And [the noise] is detrimental to their health and anxiety.” Dr. Stephen Krzeminski, another Granbury ENT, agrees. “Sonic damage is real, there’s no disputing that,” he says. Krzeminski says he believes the mine is causing “mental and physical” health issues. “Imagine if I had vuvuzela in your ear all the time,” he says.
 Trailer homes residing right next to the mine. Jake Dockins for TIME
Trailer homes residing right next to the mine. Jake Dockins for TIME
The level of noise is appalling to Dr. Thomas Münzel, a German cardiologist who is a leader in the growing field of scientific researchers measuring the impact of urban and industrial noise on humans. For the last 15 years, Münzel has studied how transportation and urban noise, especially at night, can be debilitating stressors on the heart, brain, and cardiovascular systems. In one study, he exposed young, healthy students to noise events up to 63 decibels, and found that their vascular function diminished after just a single night. In other studies, he’s found that nighttime noise pollution directly leads to heart failure and molecular changes in the brain, which may lead to impaired cognitive development of children and make some people more prone to developing dementia.
“The European Environmental Agency tells us that everything above 55 decibels is making us sick,” he says. The fact that the Granbury Bitcoin mine is emitting 70 or even 90 decibels on a nightly basis is “like torture,” he says. “The most spectacular cardiovascular diseases will develop. They have to stop the machines.”
Health effects have the potential to extend past the human residents of Granbury. Studies have shown that man-made noise pollution harms animals and wildlife, causing oxidative stress and memory loss in rodents, acute anxiety in dogs, and a decrease in forest growth. Shenice Copenhaver’s dog, Persephone, started going bald and developed debilitating anxiety shortly after the Bitcoin mine began operating four blocks away. Directly next door, Tom Weeks’ dog Jack Rabbit Slim started shaking and hyperventilating uncontrollably for hours on end; a vet placed him on the seizure medication Gabapentin. Rosenkranz’s chickens stopped laying eggs for months. And Jerry and Patricia Campbell’s centuries-old oak tree, which had served as the family’s hub and protector for generations of backyard family reunions and even a wedding, died suddenly three months ago.
It’s nearly impossible to prove the Bitcoin mine directly caused the afflictions of these specific animals and plants. But as the strange anecdotes collect, they’ve added to the stress of a town that feels under siege from all directions.
“I’ve lived in Texas all my life and I’ve never seen an oak tree be beautiful one year and die the next,” Jerry Campbell says on his lawn, beneath the tree’s gnarled, blackened limbs. “It’s so strange.”
Hood County Constable John Shirley has spent months trying to find his own solutions to a problem that at times seems supernatural. As a former member of the Oath Keepers, a far-right militia whose leaders were convicted of seditious conspiracy against the U.S. government, Shirley is a somewhat divisive figure in the town. But lately Shirley has been laser-focused on the mine—an issue he considers apolitical. “When you’ve got Greenpeace supporting the same cause as a former Oath Keeper, what weird episode of the Twilight Zone are we in?” he says, chuckling darkly. (Shirley resigned from the Oath Keepers before Jan. 6, 2021, due to “serious concerns” with the direction of the organization, he says.)
 Shenice Copenhaver’s dog, Persephone, started going bald and developed anxiety shortly after the mine began operating four blocks away. Jake Dockins for TIME
Shenice Copenhaver’s dog, Persephone, started going bald and developed anxiety shortly after the mine began operating four blocks away. Jake Dockins for TIME
On a listless May morning before the sun has risen, Shirley is sitting in his truck across the road from the mine. He is used to getting up at this hour, as he’s been taking decibel readings of the plant around the clock in order to write tickets against the mine’s operators for disorderly conduct. Shirley sticks his recorder out the window and the numbers on it flicker up and down as the roar washes over it. Eventually, the recorder caps out at 91 decibels, which the CDC estimates as roughly in between the output of a lawnmower and a chainsaw.
This level of noise, the CDC writes, can cause hearing damage after two hours of exposure. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration advises that employees can only work in 90-decibel settings for eight hours a day and are required to wear ear protection. And Texas state penal code deems any noise above 85 decibels unreasonable. Over the course of 2024, Shirley has recorded a noise above 85 decibels coming from the plant more than 35 times.
Technically there is federal mandate to regulate noise, which stems from the 1972 Noise Control Act—but it was essentially de-funded during the Reagan administration. This leaves noise regulation up to states, cities, and counties. New York City, for instance, has a noise code which officially caps restaurant music and air conditioning at 42 decibels (as measured within a nearby residence). Texas’s 85 decibels, in contrast, is by far the loudest state limit in the nation, says Les Blomberg, the executive director of the nonprofit Noise Pollution Clearinghouse. “It is a level that protects noise polluters, not the noise polluted,” he says.
Ultimately, Constable John Shirley can’t stop the machines, because there is no state law forcing the operator of a noisy machine to turn it off. When Shirley writes a ticket for disorderly conduct, it merely triggers a $500 fine, as opposed to jail time or another punitive measure. Hood County can’t even pass a relevant noise ordinance law: only Texas cities, not counties, have the ability to do so.
Shirley’s tickets now add up to a theoretical fine of $17,500 and counting. But that number is chump change for Marathon, which earned $165 million in revenue in the first quarter of 2024 and bragged to shareholders about “record earnings.” And the company is fighting back: They have requested a jury trial to overturn this low-level misdemeanor, which starts July 8. At a pre-trial hearing in May, the company arrived with a full team of lawyers. “To bring two or three full-suited attorneys to a justice of the peace court citation issue: I’ve never seen that,” says Patrick Ryan, a local lawyer who has consulted with Granbury community members about the possibility of a civil nuisance lawsuit. “They’re coming with both barrels.”
A representative for Marathon declined several interview requests with TIME, saying that the company would refrain from commenting publicly until Constable Shirley’s “unwarranted” citations against the plant had been resolved. As Shirley sits outside the facility recording the pulsating drone, his nostrils flare, and his voice rises with impatience. “When I was a murder investigator and someone killed somebody, I had the law on my side,” he says. “With this, it’s like I’m swatting at a rhinoceros.” As he reads the decibel levels on his sound meter, a security guard from the facility steps out of his car and snaps pictures of Shirley’s truck in the dark.
 Shadden, who suffered from hearing loss, on her property in Granbury, Texas.Jake Dockins for TIME
Shadden, who suffered from hearing loss, on her property in Granbury, Texas.Jake Dockins for TIME
The residents of Granbury feel they’ve been lied to. In 2023, the site’s previous operators, US Bitcoin Corp, constructed a wall around the mine almost 2,000 feet long and claimed that they had “solved the concern.” But Shirley says that the complaints from the community about the sound actually increased when the wall was nearing completion last fall. Since Marathon bought the facility outright in December, its hash rate, or computational power expended, has doubled.
As complaints mounted at the top of 2024, the company contended it did not know about the extent of the sound issues. “We are now the owners, but we are not the operator. USBTC is still the operator. Prior to the purchase, we were not aware of the noise issues,” a Marathon representative wrote to TIME in an email in January. “Now that we own the site and have been made aware of the issue, we are working to gather information and address the situation.”
But documents show that Marathon provided a $67 million loan in May 2021 to the site’s first formal owners, Compute North, to build out the site’s infrastructure, and Marathon’s purchase agreement of the site, dated December 15, 2023, clearly mentions the existence of the $1.9 million “sound wall” built several months prior.
As community complaints reached a fever pitch earlier this year, Marathon held a meet-and-greet on March 29—Good Friday, which rubbed many people in Granbury’s deeply religious community the wrong way. For the handful of people that did show up, Marathon laid out a noise mitigation plan which included turning off idle fans, moving some containers into liquid cooling by April 2024, and installing vegetation and trees around the perimeter.
In an emailed statement to TIME in late June, Marathon said that 58 air-cooled containers have been removed from the site, and pointed to a roadmap which vows to convert 50% of the site’s containers to immersion cooling by the end of the year. A representative for Constellation Energy, which owns the power plant that Marathon connects to, said in a statement that the company is “staying updated on [Marathon’s] efforts to respond to the concerns raised by neighbors… We will continue working closely with Marathon as they take actions to reduce their impacts.”
Marathon says that immersion cooling, in which computers are placed in tubs of oil, will largely fix the noise problem. But the technique has potential drawbacks, including the difficulty of regularly performing maintenance on a computer submerged in oil, says Kent Draper, the chief commercial officer of the Bitcoin and AI data center operator IREN. “Although it’s been around for a long time in the industry, it’s just not that widely adopted,” he says.
Even Marathon expressed skepticism about its ability to convert its many machines to immersion technology in a 2023 year-end SEC Report. “There is a risk we may not succeed in developing or deploying immersion-cooling at such a large scale to achieve sufficient cooling performance,” the company wrote.
In an email to TIME, Marathon wrote: “While we are confident in our ability to scale this new technology, it is our obligation, as a publicly traded company, to identify any potential risks from a financial perspective.”
 A representative for Marathon Digital Holdings says the company is transitioning to a quieter form of cooling. Jake Dockins for TIME
A representative for Marathon Digital Holdings says the company is transitioning to a quieter form of cooling. Jake Dockins for TIME
Granbury community members are exploring political and legal avenues. A petition against the mine in Granbury and its “excessive and unhealthy noise” garnered 800 in-person signatures, and was brought by representatives to the Texas Republican state convention in San Antonio in May, with the hopes of gaining statewide support for some sort of ban. But two local elected officials, Nannette Samuelson and Shannon Wolf, say they tried to take the floor to stump for the issue, but weren’t given time to speak. Samuelson’s goal is now to pass resolutions in commissioners court prompting state senators to draft legislation.
Any statewide legislation is sure to hit significant headwinds, because the very idea of regulation runs contrary to many Texans’ political beliefs. “As constitutional conservatives, they have taken our core values and used that against us,” says Demetra Conrad, a city council member in the nearby town of Glen Rose.
Some community members are also exploring a potential civil nuisance suit against Marathon, in which they would seek an injunction against the company and/or damages. One affected woman, Cheryl Shadden—who has medically-documented hearing loss—has retained the nonprofit Earthjustice to examine potential litigative routes. Deputy managing attorney Mandy DeRoche says Earthjustice is exploring the possibility of taking its own sound readings near the site. The nonprofit has been involved in several lawsuits against crypto mining companies across the country.
“Historically, Bitcoin miners go to the cheapest source of electricity with the least amount of regulation, and they do the cheapest thing possible,” DeRoche says. “It’s one of the reasons why noise pollution from crypto mining tends to be so much worse than traditionally-operated data center operators.”
As Bitcoin continues to gain value, miners are building progressively bigger operations, causing gas plants and other fossil fuel emitters to spring back into action. It is unclear whether states even have the energy capacity to support this new demand: In June, Texas lieutenant governor Dan Patrick tweeted that Texans “will ultimately pay the price” for the growth of crypto and AI data centers, writing that they “produce very few jobs compared to the incredible demands they place on our grid.” Regardless, Bitcoin lobbying groups are attempting to pass pro-Bitcoin-mining bills in state legislatures across the country, which would exempt similar operations from noise ordinances and local zoning laws. People have reported similar symptoms near Bitcoin mines in Arkansas and Williston, North Dakota. Ultimately, Granbury is just one canary of several in the proverbial mine.
In the week before this article’s publication, two more Granbury residents suffered from acute health crises. The first was Tom Weeks, the owner of the hyperventilating dog. On July 2, Weeks, 64, rose after another sleepless night of listening to the mine and realized he couldn’t breathe. He was rushed to a Fort Worth hospital, where he was diagnosed with a pulmonary embolism—a blood clot blocking his lungs—and hooked up to an oxygen tank. Weeks was supposed to testify against Marathon in the jury trial, but is now physically unable to do so. “This whole thing is an eye opener for me into profit over people,” Weeks says in a phone call from the ICU.
The second person affected was the five-year-old Indigo Rosenkranz. On July 6, she suffered from a seizure and was taken to the emergency room, before being routed to a childrens’ hospital in Fort Worth for further testing. Her mother, Sarah, was terrified and now feels she has no choice but to get a second mortgage to move away from the mine. “A second one would really be a lot,” she says. “God will provide, though. He always sees us through.”
Bitcoin
Bitcoin (BTC) Price Drops Below $65K After FOMC as Middle East Tensions Rise
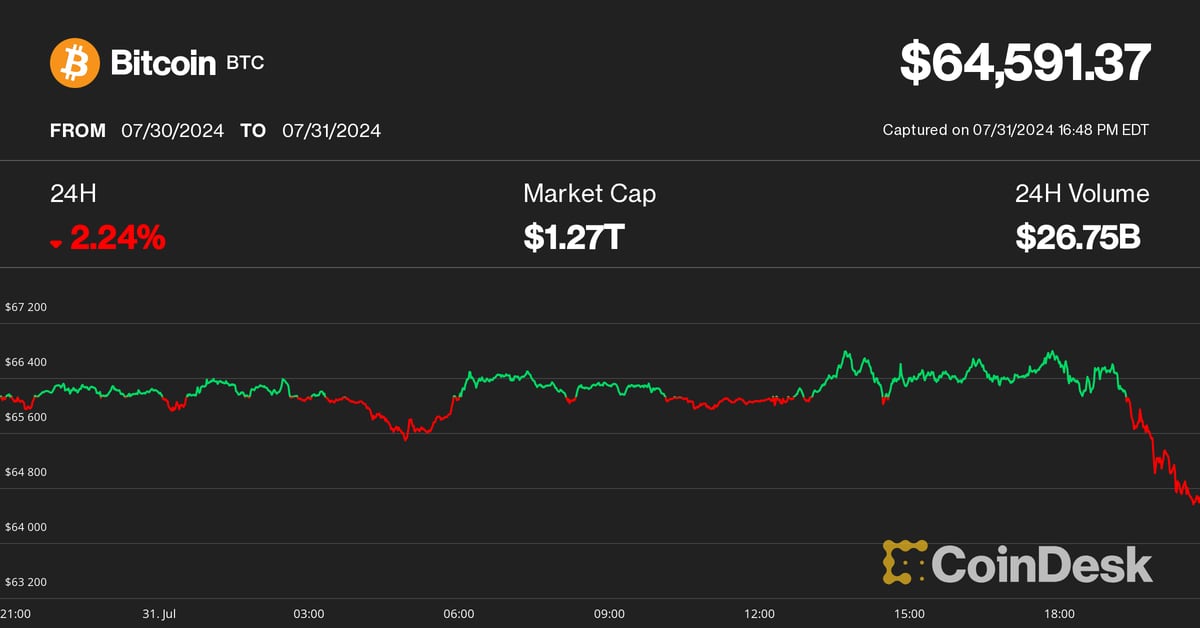
Cryptocurrencies fell sharply on Wednesday as rising geopolitical risks captivated investors’ attention following the conclusion of the Federal Reserve’s July meeting.
Bitcoin (BTC) fell to $64,500 from around $66,500, where it traded following Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell’s press conference and is down more than 2% in the past 24 hours. Major altcoins including ether (ETH)sunbathing (SUN)Avalanche AVAX (AVAX) and Cardano (ADA) also fell, while Ripple’s XRP saved some of its early gains today. The broad cryptocurrency market benchmark CoinDesk 20 Index was 0.8% lower than 24 hours ago.
The liquidation happened when the New York Times reported that Iran’s leaders have ordered retaliation against Israel over the killing of Hamas leader Ismail Haniyeh in Tehran, raising the risk of a wider conflict in the region.
Earlier today, the Fed left benchmark interest rates unchanged and gave little indication that a widely expected rate cut in September is a given. The Fed’s Powell said that while no decision has been made on a September cut, the “broad sense is that we are getting closer” to cutting rates.
While digital assets suffered losses, most traditional asset classes rose higher during the day. U.S. 10-year bond yields fell 10 basis points, while gold rose 1.5% to $2,450, slightly below its record highs, and WTI crude oil prices rose 5%. Stocks also rallied during the day, with the tech-heavy Nasdaq 100 index rebounding 3% and the S&P 500 closing the session 2.2% higher, led by 12% gains in chipmaker giant Nvidia (NVDA).
The different performances across asset classes could be due to traders’ positioning ahead of the Fed meeting, Zach Pandl, head of research at Grayscale, said in an emailed note.
“Equities may have been slightly underutilized after the recent dip, while bitcoin is coming off a strong period with solid inflows, while gold has recovered after a period of weakness,” he said.
“Overall, the combination of Fed rate cuts, bipartisan focus on cryptocurrency policy issues, and the prospect of a second Trump administration that could advocate for a weaker U.S. dollar should be viewed as very positive for bitcoin,” he concluded.
UPDATE (July 31, 2024, 21:30 UTC): Adds grayscale comments.
Bitcoin
No, Bitcoin Will Not Solve Our National Debt

Wyoming Republican Senator Cynthia Lummis speaks at the Bitcoin 2024 conference in … [+] Nashville, Tennessee, U.S., on Saturday, July 27, 2024. Former U.S. President Donald Trump said he would fire the chairman of the Securities and Exchange Commission and pick crypto-friendly regulators if he returns to the White House in a bid to woo virtual currency enthusiasts and capitalize on the industry’s growing influence in the political arena. Photographer: Brett Carlsen/Bloomberg
© 2024 Bloomberg Finance LP
At a Bitcoin conference last weekend, Senator Cynthia Lummis (R-Wyo.) announced future legislation that would direct the Treasury to purchase 1 million Bitcoin, or roughly 5% of the global supply, over five years (which would cost between $60 billion and $70 billion at today’s prices). Lummis claimed that the federal government would be “debt-free because of Bitcoin” if his proposal were to pass, because these Bitcoins could be sold by the federal government at a profit after 20 years. Unfortunately, there are mathematical and conceptual problems that prevent such an approach from solving the federal government’s budget problems.
Let’s start with the math: US National Debt Today stands at nearly $28 trillion (or $35 trillion if you include the “intragovernmental debt” that the general fund owes to other internal government accounting entities, such as the Social Security and Medicare trust funds). This year alone, the federal government spent about $2 trillion more than it took in in revenue, which had to be covered by borrowing money that adds to our national debt.
In comparison, the total market capitalization of Bitcoin today (which is the total number of Bitcoins in existence multiplied by their current market price) is only about $1.3 trillion — and that’s with Bitcoin’s current price near its all-time high. If all the Bitcoin in the world isn’t worth enough to cover a single year’s budget deficit, there’s no way buying 5% of it could plausibly stem the growth of, let alone pay off, our national debt. For the math to work, Bitcoin’s market cap would have to reach a level that is a multiple of the annual economic output of the entire planet (the International Monetary Fund current estimates the sum of each country’s gross domestic product is less than US$110 trillion).
But beyond the math, there are serious conceptual problems with Lummis’s proposal as a partial solution. When the government acquires an asset, it is typically reallocating rather than creating wealth. As the government buys some of the existing supply of Bitcoin, it would reduce the remaining supply available for others to buy on the market. If private demand for Bitcoin remains constant, the result would be an increase in the price of one Bitcoin. The beneficiaries of this transaction would be the current owners of Bitcoin (one of whom is Senator Lummis herself), because they would be in possession of an asset that can be sold at a higher price than the price at which it was originally purchased.
The increase in Bitcoin’s price, and thus the financial benefit to current holders, is likely to be even greater because, rather than remaining constant, private demand would increase as previously cautious investors view the U.S. government’s investment as an indicator of the digital asset’s legitimacy. These higher prices would not only increase demand for Bitcoin, but could also encourage Bitcoin “miners” to increase supply. Bitcoin mining is a extremely energy intensive process that relies on advanced graphics processing units (GPUs). If Bitcoin mining increases demand for GPUs, the GPUs themselves will become more expensive, as they did in 2020. In turn, every activity that depends on GPUs — from video editing to gaming — will also become more expensive.
Perhaps most alarmingly, a boom in Bitcoin mining threatens to stifle promising developments in artificial intelligence (AI). As other Forbes contributors point out, he wroteAI has the potential to revolutionize our economy and boost the productivity of our workforce in countless ways that would increase real wealth for Americans of all socioeconomic backgrounds. But AI also relies on advanced GPUs to function, of which there are already there is not enough supply to meet demand. It would be a profound failure of federal policy to make AI advances more costly to achieve by encouraging people to spend the resources needed to generate digital tokens. Furthermore, even if federal government Bitcoin purchases do not lead to an increase in Bitcoin mining, there are still other ways in which rising Bitcoin prices would displace productive economic investment — but rather than delve into them here, I recommend reading this great 2022 article by Josh Barro about the subject.
For these and other reasons, the federal government should not take any action to push the price of Bitcoin — or any other cryptocurrency, for that matter — above the level set by the free market. If policymakers believe that prices will continue to rise anyway and want to capture some of that value for deficit reduction, there are much better mechanisms for doing so. For example, a capital gains tax increase could aim to capture 5% of the gain on 100% of Bitcoin rather than capturing 100% of the gain on 5% of Bitcoin, as the Lummis proposal would seek to do. In addition to avoiding the market-distorting effects of the Lummis proposal, this approach has the added benefit of not leaving taxpayers holding the bag if the value of Bitcoin plummets, as then many other cryptocurrencies have done.
When it comes to dealing with our national debt, there is no substitute for cutting spending and/or raising taxes. There are no quick fixes here — policymakers must accept tradeoffs and make hard choices about how to allocate limited resources. Fortunately, my team at the Progressive Policy Institute recently published a serious package of proposals that deals with these tradeoffs to put the federal budget on a path to balance within 20 years. Even adopting half of our recommended savings would allow policymakers to keep debt from growing faster than our economy, which is what most economists consider to be the measure of fiscal sustainability. And ours is just one framework: six other think tanks published their own plans to stabilize the debt last week (and notably, none of them proposed spending up to $70 billion of taxpayer funds on Bitcoin).
To Senator Lummis’s credit, she has also supported efforts to promote serious solutions like these in the past. As a member of the U.S. House of Representatives in 2012, Lummis was one of only 38 members who resisted partisan pressure and voted in favor of a congressional budget resolution based on the debt stabilization recommendations of the bipartisan Simpson-Bowles Fiscal Commission. More recently, Lummis was one of nine senators to cosponsor a bill that would establish another bipartisan fiscal commission to generate an updated package of recommendations to stabilize the national debt. It would be a great service to the nation if Senator Lummis would put all her energy into advancing these and other serious efforts to align revenues and spending rather than distracting them with alternative schemes that would merely enrich cryptocurrency investors at the expense of the taxpayer.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin Falls as ETF Flows Reverse, Mt. Gox Moves Billions

In a week of drastic fluctuations, the price of Bitcoin (BTC) has retreated from its highs and is currently trading at US$66,250, down 0.9% in European trading.
This volatility comes on the heels of a significant surge above $70,000 earlier in the week, fueled by former President Donald Trump’s ambitious cryptocurrency plans announced in a Bitcoin Conference in Nashville.
Trump’s announcement to fire Securities and Exchange Commission Chairman Gary Gensler and establish a strategic Bitcoin reserve if elected president has temporarily sent the cryptocurrency market into a frenzy.
However, the excitement was short-lived as a series of events unfolded which caused investor sentiment to sour.
A significant sell-off of about 8% was triggered when the US Marshals Service moved $2 billion in Bitcoin for new wallets.
This move has reignited fears of a potential large-scale liquidation, compounded by lingering concerns over a possible Bitcoin liquidation from Mt. Gox. Early this morning, Mt. Gox administrator transferred US$2.2 billion value of your BTC assets in a new wallet.
Meanwhile, the US Bitcoin ETF spot market is showing signs of fluctuation, according to data from SoSo Value. On July 30, Bitcoin spot funds experienced their first net outflow in five days, totaling $18.3 million.
The Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC) saw outflows of $73.6 million, while the BlackRock iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) attracted $74.9 million in inflows. But outflows from other funds left the category in the red at the end of Tuesday’s trading session. The total net asset value of spot Bitcoin ETFs currently stands at a substantial $58.5 billion.
In other crypto news, Ripple (XRP) is up 8.6% in the past 24 hours, hitting over 64 cents – its highest point since March 25, according to CoinGecko. data.
This rally comes amid a scheduled token unlock and growing optimism around a potential deal in the long-running SEC vs. Ripple lawsuit.
The crypto community is closely watching the SEC’s actions, particularly its intention to amend its complaint against Binance regarding “Third-Party Cryptocurrency Securities,” which some interpret as a positive sign for Ripple.
On a market analysis noteSingapore-based cryptocurrency trading desk QCP Capital wrote that while election headlines continue to dominate, several crucial macroeconomic events loom on the horizon.
“Election headlines will continue to be a key focus, but several key macroeconomic events are also on the horizon. Key events starting with the FOMC meeting on Wednesday, megacap tech earnings (Apple, Amazon, Meta) throughout the week, and unemployment data on Friday,” QCP Capital wrote.
Edited by Stacy Elliott.
Bitcoin
1 Top Cryptocurrency That Could Surge Over 4,300%, According to This Wall Street Firm

This bold prediction that Bitcoin will hit $2.9 million by 2050 could redefine your investment strategy.
In a groundbreaking report, VanEck, a leading investment management firm, has set the stage for an extraordinary prediction about Bitcoin‘s (BTC -2.63%) in the future. According to their analysis, Bitcoin could potentially reach a staggering $2.9 million by 2050, marking an astronomical increase of over 4,300% from its current price.
This bold prediction is more than just a headline-grabbing attempt. The report is packed with information across its 20+ pages, and includes plenty of evidence and hypotheses to support its claims. Luckily, I read the whole thing, so you don’t have to. In this article, we’ll explore the key elements of VanEck’s report, deciphering why Bitcoin’s value could skyrocket to such heights and what it means for investors and the financial world at large.
Image source: Getty Images.
Unpacking the VanEck Report
VanEck’s analysis outlines three scenarios for predicting Bitcoin’s future value: the bearish case, the base case, and the bullish case. Each scenario provides a different perspective on how Bitcoin may evolve based on various economic and technological factors, and of course, where its price may be headed.
To arrive at these conclusions, VanEck’s valuation model relies on a combination of historical data, current market trends, and future financial developments. This comprehensive approach aims to assess Bitcoin’s potential as a medium of exchange and reserve asset. With that out of the way, let’s move on to the scenarios.
Bear scenario
In the pessimistic case, Bitcoin’s value is expected to remain relatively stagnant, reflecting limited growth due to regulatory hurdles, technological limitations, or broader economic challenges.
This scenario assumes that Bitcoin will not achieve widespread adoption and will face significant competitive threats from other digital currencies or innovations. If this is the path Bitcoin takes, VanEck predicts that Bitcoin will only reach $130,314 by 2050. This equates to a measly 2.6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
Base scenario
The base case presents a more balanced view, where Bitcoin’s value is influenced by moderate adoption and integration into the existing financial system. However, even though it is called the base case, it is still extremely bullish.
This analysis predicts that Bitcoin will reach a price of $2,910,345 and solidify itself as a viable digital asset, resulting in a stronger CAGR of close to 15.7%. Driving this adoption are a multitude of factors, such as rising government debt around the world, reduced use of fiat currenciesbetter technology that makes Bitcoin faster and cheaper to use, and the possibility of Bitcoin becoming the world’s reserve currency.
Bullish scenario
The bullish scenario is the most optimistic, predicting that Bitcoin’s value could reach a staggering $52,386,207 by 2050. Here, Bitcoin’s CAGR rises to 29.3%.
This extreme growth projection is based on Bitcoin achieving widespread adoption as a medium of exchange and a reserve asset. It considers advances in blockchain technology, significant macroeconomic changes, and increased institutional investment. In short, this scenario basically assumes that the world will undergo hyper-Bitcoinization very quickly.
How Bitcoin Could Reach $2.9 Million
While the bear and bull scenarios are unlikely outliers on either end of the spectrum, it’s worth examining the reasoning behind VanEck’s base result in greater detail. This intermediate target strikes a valuable middle ground and does a good job of capturing what makes Bitcoin so unique.
The first catalyst that could send Bitcoin to nearly $3 million is increased adoption as a medium of exchange. As the world and its financial system become more digitized, there is a clear path where Bitcoin could gain traction as a popular medium of exchange. The decentralized nature of the cryptocurrency, coupled with its growing acceptance among merchants and consumers, supports its potential to become a mainstream payment method. If Bitcoin’s use as a transactional currency becomes widespread, VanEck suggests that its value could appreciate significantly.
At a more granular level, technological advancements are critical drivers of Bitcoin’s future valuation. For most of Bitcoin’s existence, its blockchain was more than capable of handling transactions cost-effectively. However, as the years have passed and it has processed more transactions, there has been a need to find a method for Bitcoin to scale efficiently.
Fortunately, there are a number of solutions in development that attempt to make Bitcoin faster and cheaper to use, such as Lightning Network and layer 2 blockchains like Stacks (STX -3.26%). VanEck believes that if Bitcoin is able to scale properly, it will only bolster the cryptocurrency’s prospects following the base case trajectory.
Expanding a bit, VanEck posits that Bitcoin could become a global reserve asset, similar to gold, as institutional investors and nations seek a stable store of value in a turbulent economic landscape. As VanEck’s report outlines, the global financial world is currently in a state of flux.
The currencies of the most prosperous economies (the US, EU, Japan and the UK) are starting to be used less for international payments. Furthermore, these economies, which dominated for much of the last century, face a growing debt burden that could further erode the value of their currencies. VanEck’s report predicts that as this trend worsens, other nations will turn to Bitcoin due to its apolitical construction and robust fundamentals that prioritize value preservation. When all is said and done, Bitcoin could become the world’s global reserve currency, causing its price to soar as governments clamor for a share of its finite supply.
Last food for thought
VanEck’s prediction that Bitcoin could rise to over $2.9 million by 2050 represents a bold and optimistic outlook for the cryptocurrency. It may sound sensationalist, but keep in mind that virtually no one could have imagined that Bitcoin would rise from just a few cents to over $60,000 over the past 15 years.
However, as appealing as this may sound, a bit of restraint is in order. No one has a crystal ball, and while the outlook is promising, investors should carefully weigh the rewards against the risks and, more importantly, Approaching Bitcoin with a long-term perspective.
But for those who believe in its future potential, have an appetite for risk, and are comfortable holding for the long term, Bitcoin’s current value could represent an attractive entry point. See you in 2050.
-
 News1 year ago
News1 year agoBitcoin (BTC) price recovery faces test on non-farm payrolls
-

 Bitcoin11 months ago
Bitcoin11 months ago1 Top Cryptocurrency That Could Surge Over 4,300%, According to This Wall Street Firm
-

 Altcoins11 months ago
Altcoins11 months agoOn-chain data confirms whales are preparing for altcoin surge with increased buy orders
-

 Bitcoin11 months ago
Bitcoin11 months agoThe US government may start accumulating Bitcoin, but how and why?
-
 News1 year ago
News1 year agoNew ByBit Listings for 2024: 10 Potential Listings
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year ago11 Best Crypto TikTok Accounts & Influencers in 2024
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year ago11 Best Shitcoins to Buy in 2024: The Full List
-

 Altcoins1 year ago
Altcoins1 year agoMarket giants have taken action!
-

 Ethereum1 year ago
Ethereum1 year agoTop Meme Coins by Market Capitalization in 2024
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year ago1.08 Trillion SHIBs Dumped on Major Crypto Exchange, What’s Going On?
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year ago19 Best Crypto Games to Play in 2024
-

 Altcoins1 year ago
Altcoins1 year agoAltcoin Recommended by Crypto Expert for Today’s Portfolio





